Abstract
CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CART19) therapy has been remarkably successful in treating a subset of patients with hematological malignancies. However, it is associated with significant toxicities, including cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity (NT). Furthermore, the rate of durable responses after CART19 therapy is low, and most patients develop resistance to the therapy. One of the predominant mechanisms for CART cell resistance is intrinsic T cell dysfunction which leads to a suboptimal CART product. The Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to favorably modulate CART phenotype and function through downregulation of inhibitory receptors and enhancement of CART cell efficacy in preclinical models and early clinical studies. However, ibrutinib is an irreversible receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor, and thus there are concerns that it inhibits CART cell proliferation and expansion. In contrast to ibrutinib and other BTK inhibitors, vecabrutinib has recently emerged as a potent, reversible, non-covalent BTK inhibitor that can block the activity of both wild type and C481 mutant BTK as well as interleukin-2-inducible T-cell kinase (ITK). We hypothesized that treatment with vecabrutinib improves CART19 antitumor efficacy through the reversible inhibition of BTK/ITK, independent of its antitumor effect.
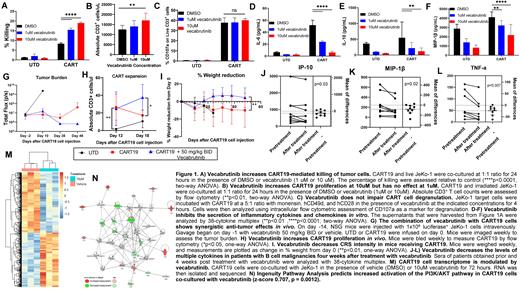
To test this hypothesis, we assessed whether vecabrutinib potentiates CART19 cytotoxicity against CD19 + tumor cells. Killing of the CD19 + mantle cell lymphoma cell line, JeKo-1, was significantly increased when CART19 were combined with vecabrutinib (Fig. 1A). Of note, vecabrutinib did not induce antitumor activity in this model as a single agent (Fig. 1A). In addition, vecabrutinib (10 µM) treatment of CART19 resulted in enhanced antigen-specific proliferation (Fig. 1B).
Next, we aimed to study the direct impact of vecabrutinib on CART19 cytokine production. We measured the levels of multiple pro-inflammatory cytokines in the supernatant of CART19 co-cultured for 3 days with JeKo-1 cells and vecabrutinib. Vecabrutinib did not impair CART19 degranulation, as measured by flow cytometric assessment of CD107a expression (Fig. 1C). Cytokines known to play a crucial part in the development of CRS, such as IL-6, IL-10, and MIP-1β were significantly downregulated in cocultures with vecabrutinib (Fig. 1D-F).
We then investigated whether the addition of vecabrutinib to CART19 caused a synergistic antitumor effect in vivo. We used our established JeKo-1 lymphoma xenograft models. Here NSG mice were engrafted with CD19 + luciferase + JeKo-1 cells. Mice were then imaged for engraftment and randomized to treatment with 1) untransduced control T cells, 2) CART19 with vehicle, or 3) CART19 with vecabrutinib 50 mg/kg BID administered via oral gavage over a period of 4 weeks. Vecabrutinib combination with CART19 treatment led to sustained antitumor activity (Fig.1G) and increased CART19 proliferation (Fig.1H). Encouragingly, mice treated with vecabrutinib better maintained their body weight following CART19 infusion, suggesting possibly dampened toxicity (Fig.1I).
We also measured serum cytokine levels from patients on a phase 1 clinical trial (NCT03037645) testing vecabrutinib in B cell malignancies at baseline and four weeks after treatment. We found that vecabrutinib significantly reduces the levels of multiple pro-inflammatory cytokines linked to CART cell toxicity, including MIP-1β, IP-10, and TNF-a (Fig. 1J-L), further validating our preclinical findings.
Finally, we interrogated the transcriptome of CART19 co-cultured with JeKo-1 with or without vecabrutinib. Total RNA sequencing of activated CART19 highlighted a significant enhanced expression of multiple genes involved in the PI3K/AKT and Th1 pathways compared to antigen stimulated CART19 alone (Fig.1M, N). These results could explain the enhanced proliferation and cytotoxicity induced by vecabrutinib.
In summary, we demonstrate for the first time that using the reversible BTK inhibitor, vecabrutinib, is a potent and a novel strategy to favorably modulate CART19 function by increasing their efficacy and decreasing toxicity. Further studies are currently underway to compare the effect of reversible versus irreversible BTK/ITK inhibition on CART functions and to further validate the mechanisms responsible for the observed effects.
Sakemura: Humanigen: Patents & Royalties. Cox: Humanigen: Patents & Royalties. Fox: Sunesis Pharmaceuticals: Current Employment. Ding: Merck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Octapharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; DTRM: Research Funding. Parikh: Pharmacyclics, MorphoSys, Janssen, AstraZeneca, TG Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, AbbVie, and Ascentage Pharma: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Verastem Oncology, and AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Kay: MEI Pharma: Research Funding; Sunesis: Research Funding; Rigel: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AstraZeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; CytomX Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Juno Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Meyer Squib: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Behring: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Research Funding; Morpho-sys: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Targeted Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Tolero Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Dava Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Acerta Pharma: Research Funding; Agios Pharm: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Oncotracker: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Kenderian: Humanigen, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal